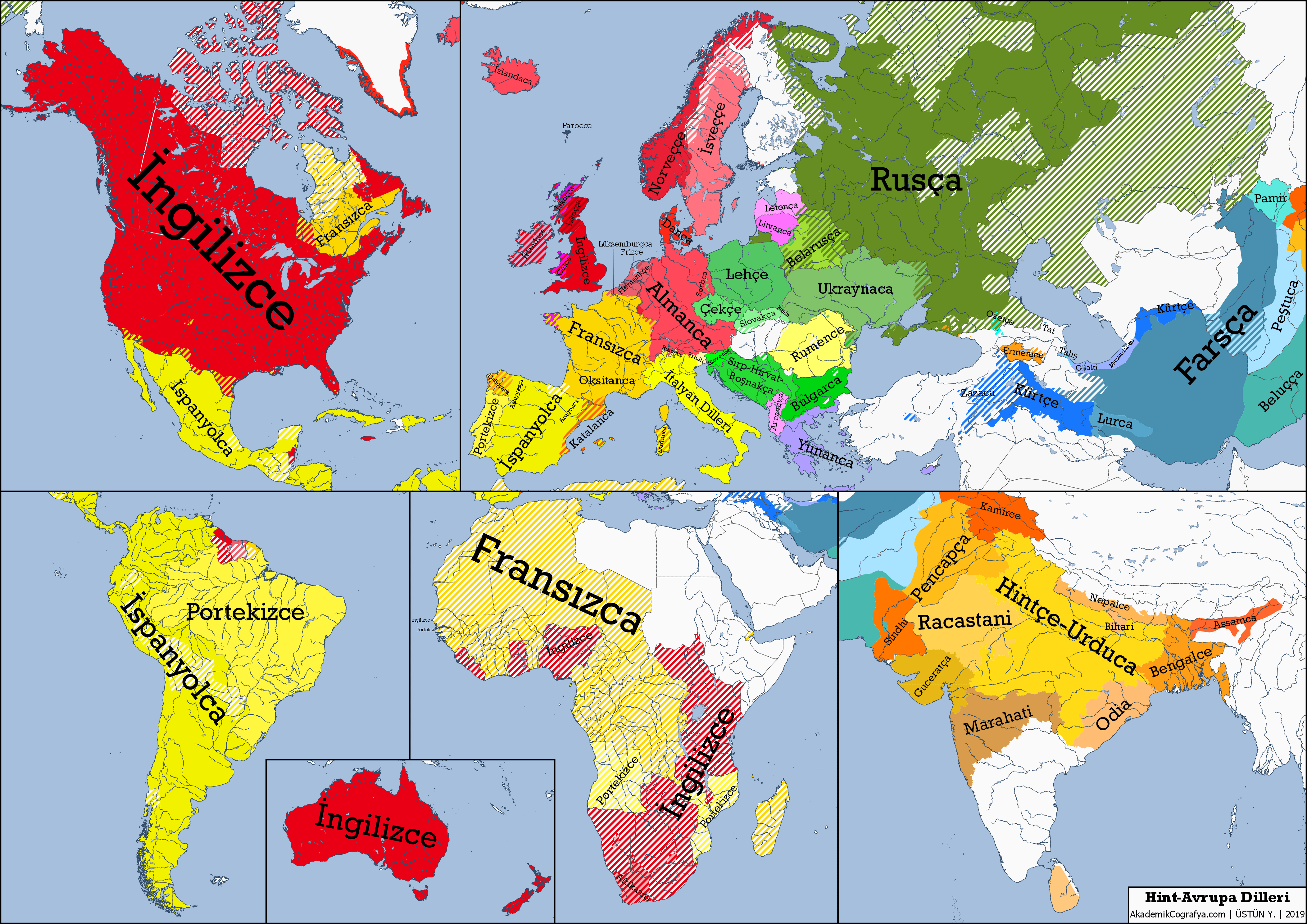
Indo-European languages represent a fascinating family of over 400 languages, which is spoken today by more than 40% of the world’s population. Recent landmark studies have traced the roots of these languages back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who lived in what is now Russia approximately 6,500 years ago. These linguistic pioneers, associated with the Yamnaya culture, significantly influenced the spread of language and culture across vast regions, from Europe to South Asia. Genetic studies have confirmed these origins, connecting ancient pastoralists to modern populations through rigorous analyses in historical linguistics. As researchers uncover more about the origin of Indo-European languages, the impact of these findings resonates deeply in our understanding of human migration and cultural evolution.
The Indo-European language family encompasses a rich tapestry of dialects and tongues that have shaped human communication for millennia. Often referred to in studies of historical linguistics, these languages trace back to early cultures such as the ones found among the Yamnaya and their ancestors in the Eurasian steppe. The interplay of genetics and language has provided new insights into the Caucasus Lower Volga population, which is credited as one of the likely sources of this influential language group. Understanding the migration patterns and genetic links among ancient peoples enriches our grasp of how these languages spread across Europe and Asia, presenting an intricate picture of human history. This exploration opens up further inquiries into the cultural and social dynamics of the populations whose languages and identities have persisted through centuries.
The Origin of Indo-European Languages
The search for the origin of Indo-European languages has long puzzled linguists and historians alike. Recent studies have traced these languages back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people, which places the root of this vast language family in present-day Russia approximately 6,500 years ago. This new evidence relies heavily on DNA analysis, allowing researchers to construct a clearer understanding of ancient human migrations and sociolinguistic developments that contributed to the diversity of languages we see today.
Understanding the origins of these languages not only gives insight into historical linguistics but also begins to piece together the cultural contexts of their speakers. As researchers delve deeper into genetic studies, such as those involving the Yamnaya culture, a clearer narrative emerges. These cultural exchanges likely facilitated the dispersal of languages, transforming linguistic landscapes across Europe and parts of Asia.
The Role of the Yamnaya Culture
The Yamnaya culture stands out as a significant contributor to the spread of Indo-European languages, particularly through their innovations in pastoralism and mobility. As pioneers in herding and the use of oxen-towed wagons, the Yamnaya people revolutionized their way of life, allowing them to traverse vast territories. This mobility enabled not only the exchange of goods but also the dissemination of their language and culture across a range of geographical regions from Mongolia to Ireland.
Their genetic footprint, as outlined in landmark studies, highlights how the Yamnaya culture intermingled with various populations along their migration routes. This blending of cultures further enriched the linguistic diversity, leading to the emergence of different branches of Indo-European languages that we can still trace today. The ongoing research into genetic markers continues to shed light on how this nomadic lifestyle possibly influenced early forms of communication and societal structure in the regions they inhabited.
Genetic Studies and Indo-European Ancestry
Recent genetic studies have brought to light the complex ancestry of the Indo-European speaking populations. By analyzing ancient DNA from archaeological sites, researchers have been able to map out the migrations and interrelationships of ancient peoples, such as the Yamnaya and Caucasus Lower Volga groups. These studies not only illustrate the genetic continuity across regions but also depict a history of population mixtures that played a pivotal role in shaping modern European populations.
Through methods like genomic sequencing, scientists have detected variations that can be traced back to the Yamnaya ancestry within the broader Indo-European framework. The implications of these findings underscore the importance of genetic research in historical linguistics, offering explanations for language spreads and the underpinnings of cultural identity tied to language.
Linguistic Evidence of Proto-Indo-European
The linguistic evidence supporting the existence of a proto-Indo-European language has historically been a topic of intrigue among scholars. Linguists initially identified relatable characteristics among languages such as Latin, Greek, and Sanskrit, leading to the hypothesis of a common ancestor. This line of inquiry has persisted for over two centuries, culminating in recent studies that tie linguistic reconstructions with genetic evidence from ancient populations, painting a more comprehensive picture of early language dispersals.
As researchers like David Anthony have highlighted, understanding how early communities communicated can inform us about their social structures and cultural exchanges. The blending of linguistic features as groups interacted creates a rich tapestry of language evolution. The contemporary linguistic landscape is a direct reflection of these ancestral narratives, enriched by diverse influences that have emerged over millennia.
Challenges in Indo-European Studies
The field of Indo-European studies faces numerous challenges, particularly due to geopolitical factors that affect collaboration among researchers. For instance, the ongoing Russia-Ukraine war has impeded joint research efforts and data sharing, complicating the interpretation of genetic findings related to the origins of these languages. Nevertheless, the research community remains committed to uncovering the complexities of these ancient languages, developing methods that allow for safer and more effective cooperation across borders.
Additionally, as researchers sift through layers of archaeological and genetic evidence, they confront difficulties in drawing definitive conclusions regarding linguistic roots. The diverse findings arising from different locales can sometimes contradict established theories, adding to the complexity of reconstructing the narrative of Indo-European language evolution. This requires a commitment to interdisciplinary approaches that integrate historical linguistics, genetics, and archaeology to arrive at a more holistic understanding.
Cultural Practices of Indo-European Ancestors
Beyond language, the cultural practices involved in the daily lives of Indo-European speakers provide valuable insights into their societal structures and customs. Archaeological findings, such as burial mounds known as kurgans, reveal significant aspects of their rituals and lifestyles. The manner in which they interred their dead provides a glimpse into their beliefs and the social hierarchies that existed within these early communities.
The Yamnaya people’s burial practices, similar to those of their Caucasus Lower Volga ancestors, reflect the continuity of cultural traditions over generations. Researchers like Iosif Lazaridis emphasize the importance of such practices for understanding the continuity of human behavior and cultural identity through time. By studying these aspects, we can better appreciate how the cultural heritage established by these ancient peoples has influenced subsequent civilizations.
Linguistic Reconstructions and Archaeological Correlation
Linguistic reconstructions play a vital role in piecing together the history of Indo-European languages. By employing comparative methods, linguists can trace the evolution of phonetics and semantics across various language branches. This meticulous process often reveals historical patterns that align with archaeological evidence, allowing for more robust conclusions regarding the migrations and interactions of ancient peoples.
As archaeo-linguistic studies unfold, scholars increasingly rely on innovative methodologies that incorporate both genetic and archaeological findings. For instance, understanding the correlation between ancient settlements and linguistic shifts can illuminate how languages evolved in response to changes in demographics and cultural exchange. The integration of multiple disciplines creates a richer narrative of the past, allowing for deeper insights into the shared heritage of Indo-European languages.
Interdisciplinary Approaches to Language Origins
The exploration of Indo-European language origins benefits from interdisciplinary collaboration, combining the fields of genetics, archaeology, and linguistics. This comprehensive approach allows for a more nuanced understanding of how ancient societies functioned and interacted. As geneticists unravel the DNA of ancient populations, linguists analyze how language might have evolved in tandem with migration patterns, creating an intricate web of connections that traces back thousands of years.
Institutions like Harvard have spearheaded this research, bringing together diverse experts to share knowledge and conduct joint studies. Such collaborations not only enrich the scientific dialogue surrounding Indo-European languages but also pave the way for future discoveries that might redefine existing paradigms in linguistics. By working across disciplines, researchers can address complex questions about human history that are otherwise difficult to untangle.
Implications of Research Findings
The identification of the Caucasus Lower Volga people as key figures in the origin of Indo-European languages has profound implications for our understanding of human history and linguistic development. These findings shift the narrative toward recognizing the significance of specific geographic locations and cultural practices in shaping language trajectories. The recognition of such a pivotal population underscores the interconnectedness of cultural and genetic heritage.
As knowledge expands regarding ancient civilizations and their contributions to modern societies, the implications of these research findings resonate far beyond academic circles. They invite us to reevaluate how we perceive cultural identity and language today. The legacies of these ancient peoples continue to influence contemporary societies, demonstrating the enduring impact of linguistic and cultural evolution throughout history.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the origin of Indo-European languages and who were the Caucasus Lower Volga people?
The origin of Indo-European languages can be traced back to a group known as the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who lived in present-day Russia around 6,500 years ago. These ancient people spoke an ancestor tongue that eventually evolved into the Indo-European family, which now encompasses over 400 languages spoken by 40% of the world’s population.
How did the Yamnaya culture contribute to the spread of Indo-European languages?
The Yamnaya culture, emerging from the Caucasus and lower Volga region, played a pivotal role in the dissemination of Indo-European languages. Around 5,000 years ago, they began migrating across vast distances from their homeland, bringing their language with them. This migration facilitated the spread of the proto-Indo-European languages across Europe and into regions like the Indian subcontinent.
What insights have genetic studies provided regarding Indo-European languages?
Genetic studies have significantly advanced our understanding of Indo-European languages by revealing the ancestry of populations that contributed to these languages. Findings suggest that the Caucasus Lower Volga people, primarily the Yamnaya, intermixed with local populations, creating genetic markers that correlate with the spread of Indo-European languages across Eurasia.
Who were the original speakers of Indo-European languages according to historical linguistics?
According to historical linguistics, the original speakers of Indo-European languages were likely the Caucasus Lower Volga people, associated with the Yamnaya culture. This conclusion stems from a combination of linguistic reconstruction and archaeological evidence that points to their presence in the Eurasian steppe, where they developed and propagated their language.
What role did archaeology play in the study of Indo-European languages and their origins?
Archaeology has played a crucial role in studying the origins of Indo-European languages by providing insight into the cultural practices of ancient peoples like the Yamnaya. Excavations of burial mounds (kurgans) and artifacts have helped researchers trace the genetic and linguistic lineage of these groups, corroborating the findings of historical linguistics and genetics.
What connection exists between Indo-European languages and ancient Anatolian languages?
There is a significant connection between Indo-European languages and ancient Anatolian languages, as linguists believe that the latter represents an early divergence from proto-Indo-European. Recent studies indicate that both language groups may have descended from a common ancestry linked to the Caucasus Lower Volga people, illustrating the complex network of language evolution in this region.
What impact have recent discoveries had on our understanding of Indo-European languages?
Recent discoveries have revolutionized our understanding of Indo-European languages by revealing a unified genetic ancestry involving the Caucasus Lower Volga people and the Yamnaya. This genetic picture enhances our comprehension of how these languages spread and evolved, linking ancient populations in Russia and beyond in the story of linguistic development.
| Key Study Elements | Details |
|---|---|
| Origin of Indo-European Languages | Identified as originating from the Caucasus Lower Volga people in present-day Russia, around 6,500 years ago. |
| Significance of Researchers | Led by David Reich, alongside Nick Patterson and Iosif Lazaridis, successfully linking genetic data with historical linguistics. |
| Cultural Practices | Yamnaya people practiced kurgan burial customs, which links them back to Caucasus Lower Volga ancestors. |
| Geographical Spread | The Yamnaya expanded from the steppes of southern Russia to regions across Europe and into the Indian subcontinent. |
| DNA Analysis | Utilized ancient DNA from over 400 samples to confirm lineage connections between ancient populations and modern language speakers. |
| Impact and Challenges | The ongoing war in Ukraine complicates collaborative research, affecting data gathering from both Russian and Ukrainian scholars. |
| Broader Context | These findings provide an unprecedented genetic picture that integrates the evolution of over 400 Indo-European languages. |
Summary
Indo-European languages have a rich history that traces back to the Caucasus Lower Volga people, who are recognized as the ancestral speakers of this vast language family. Recent groundbreaking studies have pieced together genetic evidence that enriches our understanding of how these languages spread across Europe and Asia. The collaborative efforts among scholars and advances in DNA research have not only clarified linguistic development but also illuminate the cultural practices of early populations. Despite the geopolitical challenges, this research represents a significant leap towards unveiling the complexities of Indo-European languages’ origins.