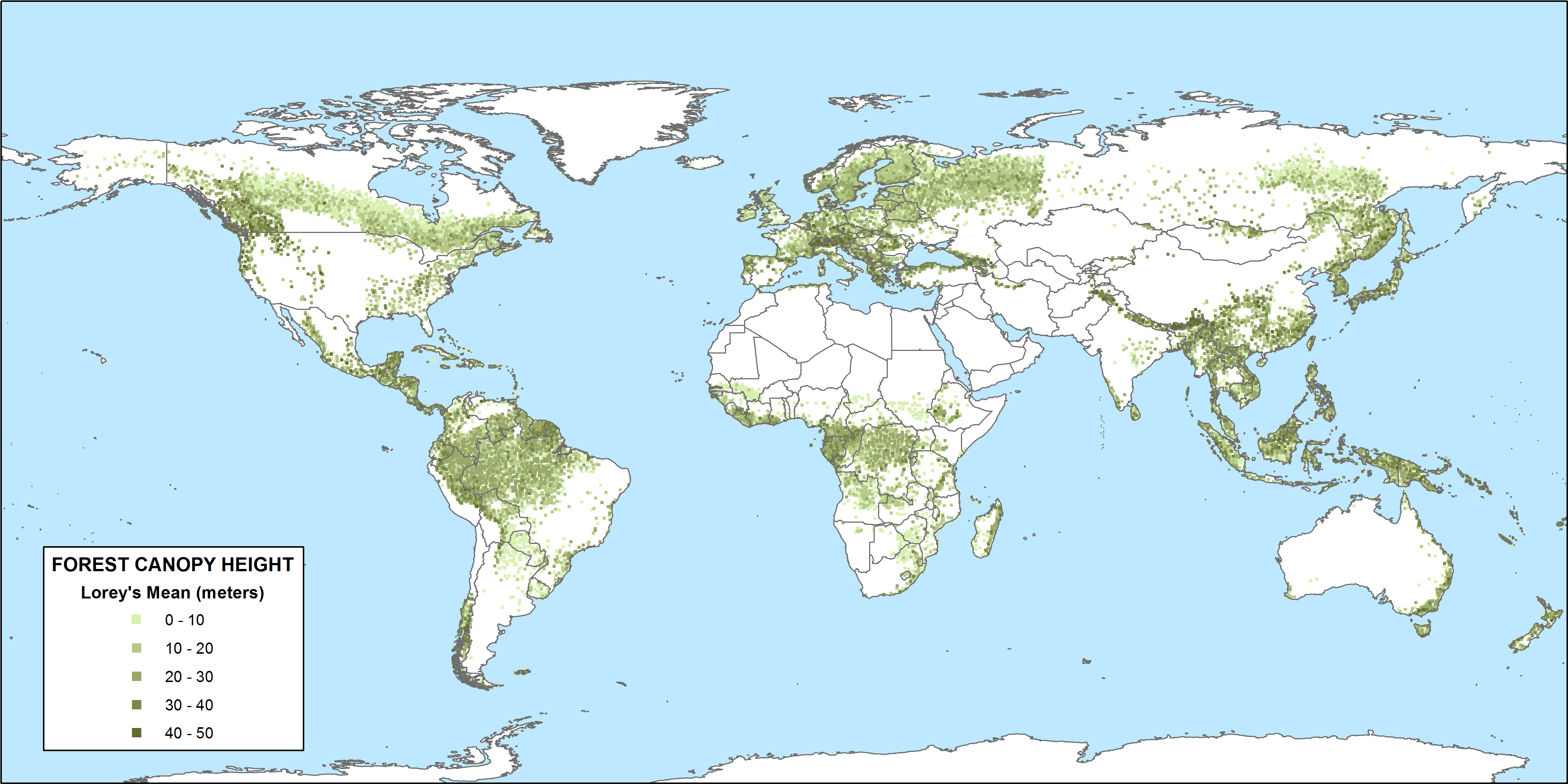
Tropical forest canopy height plays a pivotal role in understanding the health and resilience of these vital ecosystems. As global temperatures rise due to climate change, the structural integrity of these canopies can be severely impacted, affecting carbon storage capabilities and overall forest productivity. Researchers utilizing NASA’s Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) technology have made significant advancements in measuring this canopy height, providing crucial insights into the state of tropical forests worldwide. This study emphasizes the importance of tall canopies, which not only serve as indicators of forest health but also as buffers against climatic extremes. By analyzing variations in canopy height across continents, we can better understand the intricate dynamics of tropical ecosystems and their response to environmental changes.
The height of the upper layers of tropical forests, often referred to as the forest canopy, is crucial for ecological balance and biodiversity. In these lush habitats, the canopy acts as a protective cover, influencing everything from local climates to the survival of numerous plant and animal species. Recent studies leveraging advanced satellite technology have highlighted how these forest heights are linked to significant factors such as climate variability and soil conditions. The relationship between canopy structure and forest health cannot be overstated, as taller canopies are associated with enhanced carbon capture, making them indispensable in the fight against climate change. Understanding the dynamics of canopy height across various tropical regions is essential for developing effective conservation strategies and ensuring the sustainability of these critical environments.
Tropical Forest Canopy Height and Its Importance
The height of the tropical forest canopy plays an essential role in maintaining the health of these ecosystems. Generally, taller canopies are associated with increased carbon storage and higher above-ground biomass, which are critical for combating climate change. When forest canopies are healthy, they can effectively buffer the microclimate, regulate temperatures, and promote biodiversity, making them vital for both ecological balance and mitigating global warming. This height serves as a crucial indicator of overall forest health and ecological productivity.
Recent research utilizing NASA’s Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) has provided unprecedented insight into how climate change affects canopy height across tropical regions. Identifying variations in canopy height is imperative, as it helps determine how these regions respond to environmental changes and assess their potential for carbon sequestration. Understanding these dynamics allows scientists and policymakers to better protect and manage tropical forests, which are pivotal for the planet’s climate health.
Impact of Climate Change on Tropical Ecosystems
Climate change poses a significant threat to tropical ecosystems, particularly affecting forest canopy height. Factors like prolonged dry seasons and elevated temperatures can drastically alter the structure of these vital forests, which in turn affects their ability to store carbon. According to Liu’s study, the southern Amazon region is especially vulnerable, with predictions indicating further reductions in canopy height due to anticipated climatic shifts. This not only threatens the biodiversity these forests support but also undermines their function as ‘Earth’s lungs.’
Moreover, various environmental factors, including topography, soil properties, and climate conditions, contribute to the spatial variation in forest canopy height. By analyzing these factors through advanced LiDAR technology, researchers can pinpoint the most vulnerable forest areas and develop targeted conservation strategies. Recognizing how climate change impacts forest health is vital to formulating effective climate policies and ensuring the longevity of tropical ecosystems, which are essential for global climate stability.
NASA’s GEDI and Its Role in Forest Research
NASA’s Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) uses LiDAR technology to gather detailed information about forest canopies from space. This innovative tool enables scientists to map the vertical structure of forests, allowing for a comprehensive assessment of forest health, carbon storage capabilities, and susceptibility to climate changes. The ability to measure large forest expanses in a relatively short timeframe has transformed our understanding of how environmental factors influence forest ecosystems worldwide.
The data collected by GEDI is instrumental in tracking shifts in forest canopy height related to climate change, providing vital information that can shape conservation efforts. As researchers like Liu aim to expand the application of GEDI beyond primary forests, the technology’s implications for the management and protection of both tropical and temperate forests become increasingly significant. This could lead to better-informed climate policies that prioritize the preservation of these critical habitats.
Climate Effects on Forest Canopy Variation
One of the key findings of the recent study using GEDI technology highlights how crucial climate factors, such as dry season length and solar radiation, influence variations in canopy height across different tropical ecosystems. Elevated temperatures and changes in precipitation patterns can lead to diminished canopy heights, indicating stress within the forest that may affect overall ecosystem functioning. For regions like the central Amazon, moisture conditions have a significant impact on canopy structure, requiring a nuanced understanding of how climate change will potentially alter the landscape.
Understanding these environmental drivers is essential not just for local forest management but for global efforts in climate change mitigation. As canopies shrink due to the exacerbation of climate factors, their capacity for carbon storage diminishes as well. This creates a feedback loop that can intensify climate change effects, emphasizing the importance of maintaining healthy canopies for forest resiliency and carbon sequestration capabilities.
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services of Tropical Forests
Tropical forests are home to a myriad of species and provide critical ecosystem services. They harbor around 50% of the world’s terrestrial biodiversity and play a vital role in regulating climate through carbon sequestration. As the study indicates, the health of these forests is intrinsically linked to their canopy height, which serves as a habitat and sustenance for numerous organisms. This makes preserving the integrity of the canopy crucial for maintaining biodiversity.
In addition to supporting biodiversity, tropical forests provide essential services such as water filtration, soil stabilization, and climate regulation. The interdependence between canopy height and forest health highlights the urgent need for protective measures against climate change. By understanding the implications of canopy dynamics, efforts can be prioritized globally to maintain these ecosystems and mitigate the effects of climate change, which disproportionately impact tropical regions.
Monitoring Forest Health with Space Technology
The integration of spaceborne technology, such as NASA’s GEDI, into forest monitoring practices represents a significant advancement in ecological research. By providing high-resolution data on canopy structure and height, scientists can efficiently track the health of forests over time. This capability forms the backbone for understanding how climate change impacts these vital ecosystems while allowing for proactive measures in conservation.
Monitoring forest health using satellite technology not only facilitates real-time assessments but also aids in predicting future shifts in forest dynamics. The ability to analyze vast geographic areas enhances the effectiveness of conservation strategies, making it a crucial tool for addressing global climate challenges. As climate change continues to affect various ecosystems, the reliance on advanced technologies like GEDI will become increasingly important in safeguarding the planet’s natural resources.
Policies for Conserving Tropical Forests
The findings from this research underscore the pressing need for effective conservation policies aimed at protecting tropical forests. Understanding the vulnerability of different forest regions to climate change assists policymakers in prioritizing locations for conservation and restoration efforts. By focusing on areas at high risk of canopy height reduction, strategies can be implemented to bolster forest resilience against climate-induced threats.
In addition to conserving existing forests, promoting sustainable forest management practices is essential for enhancing overall forest health. This includes responsible logging practices, enforcing land use regulations, and developing programs that encourage reforestation. Addressing the impacts of climate change on tropical ecosystems through informed policy and management will ultimately contribute to global carbon storage efforts and protect biodiversity hotspots.
Future of Tropical Forest Research
The future of tropical forest research is poised to integrate advanced technology with ecological studies, aiming to deepen our understanding of these invaluable ecosystems. Researchers like Liu highlight the importance of expanding their focus beyond primary forests to include various global forest and woodland areas. This broadening scope will enrich the dataset needed to inform effective conservation policies, offering insights into how diverse ecosystems react to changing climate conditions.
As the impacts of climate change become more pronounced, continued exploration of tropical forest dynamics will be crucial in shaping sustainable practices. Engaging with local communities and stakeholders will also play a significant role in adopting policies that reflect scientific findings. Ensuring the health of tropical forests not only supports biodiversity and ecosystem services but is also a cornerstone in the global fight against climate change.
The Role of Deforestation and Land Use Change
Deforestation and changes in land use are significant threats to tropical forests, directly impacting forest canopy health and height. As human activities expand into these critical areas, the balance of these ecosystems is disturbed, leading to fragmented habitats and loss of biodiversity. This degradation exacerbates the effects of climate change, as reduced forest cover translates to diminished carbon storage capacity, which is essential for regulating global temperatures.
To combat the detrimental effects of deforestation, comprehensive land use policies must be established. Implementing sustainable land management practices that protect existing forests while promoting reforestation efforts is vital. By understanding the intricate relationships between land use, forest canopy height, and ecological health, effective strategies can be developed to preserve these essential ecosystems and their crucial roles in combating climate change.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the significance of tropical forest canopy height in relation to climate change?
Tropical forest canopy height is a crucial indicator of forest health, ecosystem productivity, and carbon storage. As climate change progresses, variations in canopy height reveal how these ecosystems are affected by factors like heat and drought, influencing their ability to sequester carbon and maintain biodiversity.
How does NASA’s GEDI technology contribute to our understanding of tropical forest canopy height?
NASA’s Global Ecosystem Dynamics Investigation (GEDI) uses LiDAR technology from the International Space Station to measure tropical forest canopy height with unprecedented detail. This data helps scientists analyze the structural variations of forests and assess the impacts of climate change on their health and carbon storage capabilities.
What environmental factors influence tropical forest canopy height according to recent studies?
Recent studies show that climate, topography, and soil properties account for nearly 75% of the variation in tropical forest canopy height. Key factors such as elevation, dry seasons, and solar radiation significantly impact the height of these canopies, affecting their capacity to store carbon and produce biomass.
Why is canopy height an important metric for assessing forest health in tropical ecosystems?
Canopy height is an important metric for assessing tropical forest health because taller canopies typically indicate higher carbon storage and greater biomass. They also play a critical role in moderating microclimates, which helps buffer against extreme weather conditions driven by climate change.
How are tropical forests in the southern Amazon affected by climate change in terms of canopy height?
Tropical forests in the southern Amazon are particularly vulnerable to climate change, with increasingly prolonged dry seasons primarily driving reductions in canopy height. This change threatens the forest’s ability to sequester carbon effectively and maintain overall ecosystem health.
What are the implications of studying canopy height for climate change policies?
Studying tropical forest canopy height has essential implications for climate change policies, as it helps identify vulnerable areas and informs conservation efforts. Protecting these ecosystems is vital for carbon storage and biodiversity, which can significantly contribute to climate change mitigation strategies.
How does canopy height variation differ in tropical forests across regions?
Canopy height variation in tropical forests can differ significantly by region. For example, in moist central Amazon regions, elevation is the primary driver of canopy height, whereas in drier regions like the southern Amazon, dry season length becomes the key determinant, highlighting the localized effects of climate change.
What future research directions does the study of tropical forest canopy height suggest?
Future research directions include expanding the assessment beyond primary forests to include diverse woodland areas, aiming to better understand how various forests respond to climate change. This research will help inform policy priorities for protecting ecosystems critical for carbon sequestration and biodiversity.
| Key Point | Description |
|---|---|
| Importance of Canopy Height | Tropical forest canopy height serves as a critical indicator of forest health and ecosystem productivity. |
| Use of NASA Technology | NASA’s GEDI LiDAR technology enables detailed tracking of changes in tropical forest canopy height globally. |
| Impact of Climate Change | Climate change significantly affects canopy height, especially in regions with prolonged dry seasons. |
| Research Findings | Elevation, dry season, and solar radiation are key factors influencing canopy height variation. |
| Vulnerability of Amazon | Southern Amazon’s forests are particularly at risk due to extended dry seasons predicted by climate models. |
| Broader Implications | Findings can guide policies for forest conservation and carbon storage to mitigate climate change. |
Summary
Tropical forest canopy height is crucial for understanding forest health and ecological functions. Recent research using NASA’s GEDI technology has unveiled the alarming impact of climate change on the canopy height of tropical forests. This study highlights that environmental factors such as climate, elevation, and soil significantly influence canopy height. Notably, regions like the southern Amazon face heightened vulnerability to climate change due to prolonged dry seasons, leading to reductions in canopy height. The findings underscore the necessity of protecting these vital ecosystems not only for their immense biodiversity but also for their essential role in carbon sequestration, which is critical in the fight against climate change.